imported>Chunbum Park |
imported>John Stephenson |
| (84 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| == '''[[Spanish missions in California]]''' ==
| | {{:{{FeaturedArticleTitle}}}} |
| ----
| | <small> |
| The '''Spanish missions in California''' comprise a series of twenty-one religious outposts and associated support facilities established by [[Spain|Spaniards]] of the Franciscan Order between 1769 and 1823, in order to spread the [[Catholic]] faith among the local Native American populations. The missions represented the first major effort by [[Europe]]ans to colonize the Pacific Coast region, and gave Spain a valuable toehold in the frontier land. The settlers introduced European livestock, fruits, vegetables, and industry into the region. European contact was a momentous event, which profoundly affected California's native peoples.<ref>Paddison, p. xiv: "''These missionaries, along with the soldiers, merchants, and settlers who emigrated to California before 1848, brought terrible changes to its Indian population''."</ref> In the end, the mission system failed in its objective to convert, educate, and "civilize" the indigenous population in order to transform the California natives into Spanish colonial citizens. <!-- need to better develop this thought train; architecture, literature, other -->Today, the missions are among the state's oldest structures and the most-visited historic monuments.<ref>California Missions Foundation</ref>
| | ==Footnotes== |
| | |
| ===Precontact=== | |
| The current prevailing theory postulates that Paleo-Indians entered the Americas in successive waves from [[Asia]] via a land bridge called "Beringia" that connected eastern [[Siberia]] with present-day [[Alaska]] (when sea levels were significantly lower, due to widespread glaciation) between about 15,000 to 35,000 years ago.<ref>Leffingwell, p. 9</ref> The remains of Arlington Springs Man on Santa Rosa Island are among the traces of a very early habitation in California, dated to the last ice age (Wisconsin glaciation) about 13,000 years ago.<ref>Jones and Klar 2007, p. 53: "''Understanding how and when humans first settled California is intimately linked to the initial colonization of the Americas''."</ref><ref>Oakley, p. 1172</ref> The first humans are therefore thought to have made their homes among the southern valleys of California's coastal mountain ranges some 10,000 to 12,000 years ago; the earliest of these people are known only from archaeological evidence.<ref>Paddison, p. 333: The first undisputable archaeological evidence of human presence in California dates back to ''circa'' 8,000 BCE.</ref><ref>Jones and Klar 2005, pp. 369-400: Recent research suggests that the Chumash may have been visited by Polynesians between 400 and 800 CE, nearly 1,000 years before Columbus reached [[North America]]. Although the concept was generally rejected for decades and remains controversial, studies published in peer-reviewed journals have given the idea greater plausibility.</ref> Over the course of thousands of years, California's diverse group of first settlers (later known as "Indians") evolved into hundreds of separate tribal groups, with an equally diverse range of languages, religions, dress, and other customs.<ref>Margolin, pp. 2-6</ref>
| |
| | |
| ''[[Spanish missions in California|.... (read more)]]''
| |
| | |
| {| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" style="width: 90%; float: center; margin: 0.5em 1em 0.8em 0px;"
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="text-align: center;" | [[Spanish missions in California#Notes|notes]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |
| |
| {{reflist|2}} | | {{reflist|2}} |
| |}
| | </small> |
Latest revision as of 10:19, 11 September 2020
After decades of failure to slow the rising global consumption of coal, oil and gas,[1] many countries have proceeded as of 2024 to reconsider nuclear power in order to lower the demand for fossil fuels.[2] Wind and solar power alone, without large-scale storage for these intermittent sources, are unlikely to meet the world's needs for reliable energy.[3][4][5] See Figures 1 and 2 on the magnitude of the world energy challenge.
Nuclear power plants that use nuclear reactors to create electricity could provide the abundant, zero-carbon, dispatchable[6] energy needed for a low-carbon future, but not by simply building more of what we already have. New innovative designs for nuclear reactors are needed to avoid the problems of the past.
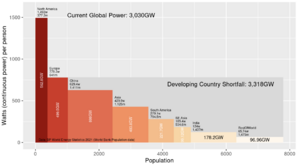
(CC) Image: Geoff Russell Fig.1 Electricity consumption may soon double, mostly from coal-fired power plants in the developing world.
[7] Issues Confronting the Nuclear Industry
New reactor designers have sought to address issues that have prevented the acceptance of nuclear power, including safety, waste management, weapons proliferation, and cost. This article will summarize the questions that have been raised and the criteria that have been established for evaluating these designs. Answers to these questions will be provided by the designers of these reactors in the articles on their designs. Further debate will be provided in the Discussion and the Debate Guide pages of those articles.
- ↑ Global Energy Growth by Our World In Data
- ↑ Public figures who have reconsidered their stance on nuclear power are listed on the External Links tab of this article.
- ↑ Pumped storage is currently the most economical way to store electricity, but it requires a large reservoir on a nearby hill or in an abandoned mine. Li-ion battery systems at $500 per KWh are not practical for utility-scale storage. See Energy Storage for a summary of other alternatives.
- ↑ Utilities that include wind and solar power in their grid must have non-intermittent generating capacity (typically fossil fuels) to handle maximum demand for several days. They can save on fuel, but the cost of the plant is the same with or without intermittent sources.
- ↑ Mark Jacobson believes that long-distance transmission lines can provide an alternative to costly storage. See the bibliography for more on this proposal and the critique by Christopher Clack.
- ↑ "Load following" is the term used by utilities, and is important when there is a lot of wind and solar on the grid. Some reactors are not able to do this.
- ↑ Fig.1.3 in Devanney "Why Nuclear Power has been a Flop"
