Anacetrapib: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk (Chem info box added) |
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|width=300px | |width=300px | ||
|molname=anacetrapib | |molname=anacetrapib | ||
|synonyms= | |synonyms= see Chemistry | ||
|molformula= C<sub>30</sub>H<sub>25</sub>F<sub>10</sub>NO<sub>3 | |molformula= C<sub>30</sub>H<sub>25</sub>F<sub>10</sub>NO<sub>3 | ||
|molmass= 637.51 | |molmass= 637.51 | ||
|uses= | |uses= cholesterol regulation | ||
|properties= | |properties= see below | ||
|hazards= | |hazards= see below | ||
|iupac= see below | |iupac= see below | ||
|casnumber= 875446-37-0} | |casnumber= 875446-37-0 | ||
} | }} | ||
In [[health care]], '''anacetrapib''' (anacet'rapib) is an oxazolidinone [[medication]] that is a cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitor that raises [[HDL cholesterol]] and reduces [[LDL cholesterol]].<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> | In [[health care]], '''anacetrapib''' (anacet'rapib) is an [[oxazolidinone]]-based [[medication]] that is a cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitor that raises [[HDL cholesterol]] and reduces [[LDL cholesterol]].<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> | ||
Anacetrapib is related to [[torcetrapib]].<ref name="pmid21082868">{{cite journal| author=Cannon CP, Shah S, Dansky HM, Davidson M, Brinton EA, Gotto AM et al.| title=Safety of Anacetrapib in Patients with or at High Risk for Coronary Heart Disease. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2010 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=21082868 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa1009744 | pmc= | url= }} </ref> | Anacetrapib is related to [[torcetrapib]].<ref name="pmid21082868">{{cite journal| author=Cannon CP, Shah S, Dansky HM, Davidson M, Brinton EA, Gotto AM et al.| title=Safety of Anacetrapib in Patients with or at High Risk for Coronary Heart Disease. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2010 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=21082868 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa1009744 | pmc= | url= }} </ref> | ||
== Chemistry and Mechanism of Action == | |||
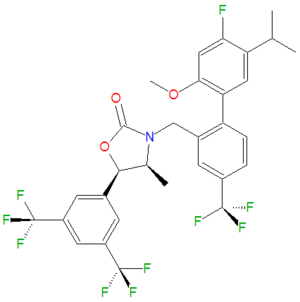
The chemical name of anacetrapib, distributed by Merck, is 2'-methoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)biphenyl-2-yl]methyl]-4-methyl-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one. It has a formula weight of 637.51 g/mol and its CAS registration number is 875446-37-0. Anacetrapib is an inhibitor of [[cholesteryl ester transfer protein]] (CETP), a key protein involved in reverse cholesterol transport, and its use increases high-density lipoprotein [[cholesterol]] ([[HDL]]). Other CETP inhibitors include [[dalcetrapib]] and [[torcetrapib]]. <ref name="pmid20406242">{{cite journal | author= Gurfinkel R, Joy TR | title= Anacetrapib: Hope for CETP Inhibitors | journal= Cardiovasc Ther | year= 2010 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=21082868 | doi= | pmc= | url= http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20406242 }} </ref>,<ref name="pmid19705341">{{cite journal| author=Mason D | title= Anacetrapib, a cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor for the treatment of atherosclrerosis | journal= Curr Opin Investig Drugs | year= 2009 | volume= 10 | issue= 9 | pages= 980-987 | pmid=19705341 | doi= | pmc= | url= http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19705341 }} </ref> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:40, 26 November 2010
|
| |||||||
| anacetrapib | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | cholesterol regulation | ||||||
| Properties: | see below | ||||||
| Hazards: | see below | ||||||
| |||||||
In health care, anacetrapib (anacet'rapib) is an oxazolidinone-based medication that is a cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitor that raises HDL cholesterol and reduces LDL cholesterol.[1]
Anacetrapib is related to torcetrapib.[2]
Chemistry and Mechanism of Action
The chemical name of anacetrapib, distributed by Merck, is 2'-methoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)biphenyl-2-yl]methyl]-4-methyl-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one. It has a formula weight of 637.51 g/mol and its CAS registration number is 875446-37-0. Anacetrapib is an inhibitor of cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), a key protein involved in reverse cholesterol transport, and its use increases high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL). Other CETP inhibitors include dalcetrapib and torcetrapib. [3],[4]
References
- ↑ Anonymous (2024), Anacetrapib (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Cannon CP, Shah S, Dansky HM, Davidson M, Brinton EA, Gotto AM et al. (2010). "Safety of Anacetrapib in Patients with or at High Risk for Coronary Heart Disease.". N Engl J Med. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa1009744. PMID 21082868. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Gurfinkel R, Joy TR (2010). "Anacetrapib: Hope for CETP Inhibitors". Cardiovasc Ther. PMID 21082868. [e]
- ↑ Mason D (2009). "Anacetrapib, a cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor for the treatment of atherosclrerosis". Curr Opin Investig Drugs 10 (9): 980-987. PMID 19705341. [e]