Mevalonate: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
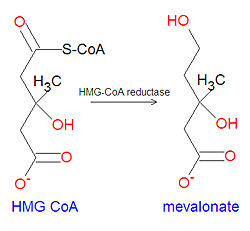
{{Image|Mevalonate synthesis.jpg|left|250px|Biosynthesis of mevalonate from HMG CoA.}} | |||
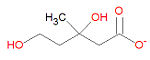
Its IUPAC chemical name is (3R)-3,5-dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoic acid and its chemical formula is C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>12</sub>O<small>4</small> in the protonated state. | Its IUPAC chemical name is (3R)-3,5-dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoic acid and its chemical formula is C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>12</sub>O<small>4</small> in the protonated state.[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:01, 18 September 2024
Mevalonate is a key chemical precursor in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. The statin drugs used to lower cholesterol are HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors that work by inhibiting the synthesis of mevalonate from the reduction of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl CoA (HMG-CoA).
Its IUPAC chemical name is (3R)-3,5-dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoic acid and its chemical formula is C6H12O4 in the protonated state.