Lovastatin: Difference between revisions
imported>Caesar Schinas mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
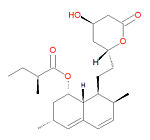
{{Image|Lovastatin structure.jpg|right|150px|Lovastatin, a type I statin.}} | |||
'''Lovastatin''', also known as '''lovastatina''' (Spanish), '''lovastatine''' (French), '''lovastatinum''' (Latin) and 6-alpha-methylcompactin, is a type I [[statin]] used to treat [[hypercholesterolemia]] (high cholesterol) and prevent [[myocardial infarction|heart attacks]] and strokes by diminishing coronary [[atherosclerosis]]. It functions by inhibiting [[3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase]]. It is a pro-drug, which only becomes active after metabolism to the active form, the <math>\beta</math>-hydroxyacid, a potent inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to [[mevalonate]]. The conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate is an early step in the biosynthetic pathway of cholesterol. It was the first drug in the class HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors class, and it is a fungal metabolite isolated from cultures of ''Aspergillus terreus''. | '''Lovastatin''', also known as '''lovastatina''' (Spanish), '''lovastatine''' (French), '''lovastatinum''' (Latin) and 6-alpha-methylcompactin, is a type I [[statin]] used to treat [[hypercholesterolemia]] (high cholesterol) and prevent [[myocardial infarction|heart attacks]] and strokes by diminishing coronary [[atherosclerosis]]. It functions by inhibiting [[3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase]]. It is a pro-drug, which only becomes active after metabolism to the active form, the <math>\beta</math>-hydroxyacid, a potent inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to [[mevalonate]]. The conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate is an early step in the biosynthetic pathway of cholesterol. It was the first drug in the class HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors class, and it is a fungal metabolite isolated from cultures of ''Aspergillus terreus''. | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
{{CZMed|Lovastatin|3767}} | {{CZMed|Lovastatin|3767}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:01, 13 September 2024
Lovastatin, also known as lovastatina (Spanish), lovastatine (French), lovastatinum (Latin) and 6-alpha-methylcompactin, is a type I statin used to treat hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol) and prevent heart attacks and strokes by diminishing coronary atherosclerosis. It functions by inhibiting 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. It is a pro-drug, which only becomes active after metabolism to the active form, the -hydroxyacid, a potent inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate. The conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate is an early step in the biosynthetic pathway of cholesterol. It was the first drug in the class HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors class, and it is a fungal metabolite isolated from cultures of Aspergillus terreus.
Its IUPAC name is [(1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxooxan-2-yl]ethyl]-3,7-dimethyl-1,2, 3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl] (2S)-2-methylbutanoate and its chemical formula is C24H36O5.
Brand names
- Altocor
- Altoprev
- Artein
- Belvas
- Cholestra
- Closterol
- Colevix
- Hipolip
- Hipovastin
- Lestatin
- Lipdip
- Lipivas
- Lipofren
- Lovalip
- Lovalord
- Lovasterol
- Lovastin
- Lozutin
- Mevacor
- Mevinacor
- Mevlor
- Monacolin K
- Nergadan
- Paschol
- Rodatin
- Rovacor
- Sivlor
- Taucor
- Tecnolip
- Teroltrat
References
External links
The most up-to-date information about Lovastatin and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Lovastatin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Lovastatin - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Lovastatin - Detailed information from DrugBank.