Tyrosine: Difference between revisions
imported>Caesar Schinas m (Bot: Update image code) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
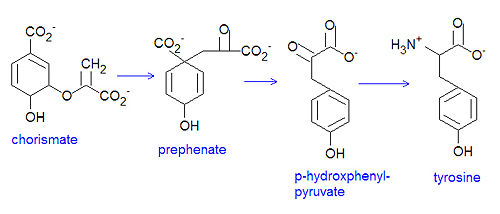
Tyrosine, an ''essential'' amino acid, is synthesised in bacteria by conversion from [[chorismate]]. A [[mutase]] converts chorismate to [[prephenate]]. Subsequent oxidative decarboxylation converts prephenate to [[p-hdyroxyphenyl-pyruvate]]. A [[transamination]] reaction of the <math>\alpha</math>-keto acid provides tyrosine. The related essential amino acid [[phenylalanine]] is similarly produced. | Tyrosine, an ''essential'' amino acid, is synthesised in bacteria by conversion from [[chorismate]]. A [[mutase]] converts chorismate to [[prephenate]]. Subsequent oxidative decarboxylation converts prephenate to [[p-hdyroxyphenyl-pyruvate]]. A [[transamination]] reaction of the <math>\alpha</math>-keto acid provides tyrosine. The related essential amino acid [[phenylalanine]] is similarly produced. | ||
[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:01, 31 October 2024
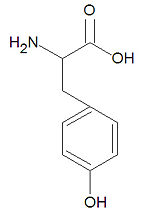
Tyrosine, abbreviated Tyr or Y, is one of the twenty common -amino acids used by living organisms to build proteins. It is one of the four aromatic amino acids together with histidine, phenylalanine and tryptophan. It is one of three amino acids subject to phosphorylation by tyrosine kinases due to the presence of a hydroxyl group, (-OH). Such phosphorylation events are central to many cell-signalling pathways. Although tyrosine is hydrophobic and the side chain is mostly buried in proteins, it is often situated such that the hydroxy group is accessible.
biosynthesis
Tyrosine, an essential amino acid, is synthesised in bacteria by conversion from chorismate. A mutase converts chorismate to prephenate. Subsequent oxidative decarboxylation converts prephenate to p-hdyroxyphenyl-pyruvate. A transamination reaction of the -keto acid provides tyrosine. The related essential amino acid phenylalanine is similarly produced.