Vardenafil: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|synonyms= Levitra® | |synonyms= Levitra® | ||
|molformula= | |molformula= | ||
|molmass= | |molmass= 579.1 (HCL form) | ||
|uses=erectile dysfunction | |uses=erectile dysfunction | ||
|properties=PDE-5 inhibitor | |properties=PDE-5 inhibitor | ||
|hazards=cardiovascular risks | |hazards=cardiovascular risks | ||
|iupac= | |iupac= see below | ||
|casnumber= | |casnumber= | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Mechanism of action == | == Mechanism of action == | ||
{{Image|CGMP.jpg|left|150px|cGMP}} | |||
By competitively binding to PDE-5 enzymes in smooth muscle and therefore inhibiting the binding of cGMP to PDE-5, the degradation of cGMP is reduced resulting in elevated levels of cGMP in the [[corpus cavernosum]] and its supply vessels. The elevated cGMP levels relax the smooth muscles, dilate the [[corporeal sinusoid]]s and increase blood flow enabling an erection. cGMP levels are normally increased during stimulation by the release of [[nitric oxide]] in the corpus cavernosum. The nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase, an enyme, which produces cGMP. Thus, vardenafil does not enhance the normal mechanism, namely increased synthesis of cGMP, but rather reduces its degradation. | By competitively binding to PDE-5 enzymes in smooth muscle and therefore inhibiting the binding of cGMP to PDE-5, the degradation of cGMP is reduced resulting in elevated levels of cGMP in the [[corpus cavernosum]] and its supply vessels. The elevated cGMP levels relax the smooth muscles, dilate the [[corporeal sinusoid]]s and increase blood flow enabling an erection. cGMP levels are normally increased during stimulation by the release of [[nitric oxide]] in the corpus cavernosum. The nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase, an enyme, which produces cGMP. Thus, vardenafil does not enhance the normal mechanism, namely increased synthesis of cGMP, but rather reduces its degradation. | ||
== Chemistry == | == Chemistry == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
Because vardenafil has vasodilator properties that result in decreased blood pressure, the combined use of vardenafil with other vasodilators, such as [[alpha-blocker]]s, must be done cautiously. Patients with a history of [[myocardial infarction|heart attack]]s, [[stroke]]s, [[arrythmia]], [[hypertension]], [[retinitis pigmentosa]] or currently on [[bosentan therapy]] should also be cautious. | Because vardenafil has vasodilator properties that result in decreased blood pressure, the combined use of vardenafil with other vasodilators, such as [[alpha-blocker]]s, must be done cautiously. Patients with a history of [[myocardial infarction|heart attack]]s, [[stroke]]s, [[arrythmia]], [[hypertension]], [[retinitis pigmentosa]] or currently on [[bosentan therapy]] should also be cautious. | ||
== | == External links == | ||
{{CZMed}} | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
{{cite journal|title=Molecular Biology and Pharmacology of PDE-5-Inhibitor Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction|author=J. D. Corbin and S. H. Sharron|journal=J. Androl.|volume=24|pages=S38-S41}} | {{cite journal|title=Molecular Biology and Pharmacology of PDE-5-Inhibitor Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction|author=J. D. Corbin and S. H. Sharron|journal=J. Androl.|volume=24|pages=S38-S41}} | ||
[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:00, 4 November 2024
|
| |||||||
| vardenafil | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | erectile dysfunction | ||||||
| Properties: | PDE-5 inhibitor | ||||||
| Hazards: | cardiovascular risks | ||||||
| |||||||
Vardenafil, commonly known by the trade name Levitra®, is a selective phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitor used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED). It is more active in vitro than the nearly identical drug sildenafil (Viagra®), but is significantly different than tadalafil, another PDE-5 inhibitor used to treat ED.
Mechanism of action
By competitively binding to PDE-5 enzymes in smooth muscle and therefore inhibiting the binding of cGMP to PDE-5, the degradation of cGMP is reduced resulting in elevated levels of cGMP in the corpus cavernosum and its supply vessels. The elevated cGMP levels relax the smooth muscles, dilate the corporeal sinusoids and increase blood flow enabling an erection. cGMP levels are normally increased during stimulation by the release of nitric oxide in the corpus cavernosum. The nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase, an enyme, which produces cGMP. Thus, vardenafil does not enhance the normal mechanism, namely increased synthesis of cGMP, but rather reduces its degradation.
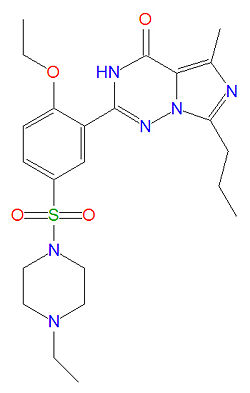
Chemistry
The IUPAC chemical name for Vardenafil HCl is piperazine, 1-[[3-(1,4-dihydro-5-methyl-4-oxo-7-propylimidazo[5,1-f ][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl)-4-ethoxyphenyl]sulfonyl]-4-ethyl-, monohydrochloride. It is a nearly colorless, solid substance with molecular mass 579.1 g/mol.
Drug interactions
Because vardenafil has vasodilator properties that result in decreased blood pressure, the combined use of vardenafil with other vasodilators, such as alpha-blockers, must be done cautiously. Patients with a history of heart attacks, strokes, arrythmia, hypertension, retinitis pigmentosa or currently on bosentan therapy should also be cautious.
External links
The most up-to-date information about Vardenafil and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Vardenafil - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Vardenafil - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Vardenafil - Detailed information from DrugBank.
References
J. D. Corbin and S. H. Sharron. "Molecular Biology and Pharmacology of PDE-5-Inhibitor Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction". J. Androl. 24: S38-S41.