Magnetic field: Difference between revisions
imported>Paul Wormer No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (44 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
In [[physics]], a '''magnetic field''' (commonly denoted by '''H''') | <br/> | ||
{{TOC|right}} | |||
In [[physics]], a '''magnetic field''' (commonly denoted by '''H''') describes a magnetic field (a vector) at every point in space; it is a [[vector field]]. In non-relativistic physics, the space in question is the three-dimensional [[Euclidean space]] <math> \mathbb{E}^3</math>—the infinite world that we live in. | |||
The | In general '''H''' is seen as an auxiliary field useful when a magnetizable medium is present. The [[magnetic flux density]] '''B''' is usually seen as the fundamental magnetic field, see the article about '''B''' for more details about magnetism. | ||
The [[SI]] unit of magnetic field strength is [[ampere]]⋅turn/[[meter]]; a unit that is based on the magnetic field of a [[solenoid]]. In the [[Gaussian units|Gaussian system]] of units |'''H'''| has the unit [[oersted]], with one oersted being equivalent to (1000/4π)⋅A⋅turn/m. | |||
The | ==Relation between '''H''' and '''B'''== | ||
The magnetic field '''H''' is closely related to the [[magnetic induction]] '''B''' (also a vector field). It is the vector '''B''' that enters the expression for magnetic force on moving charges ([[Lorentz force]]). Historically, the theory of magnetism developed from [[Coulomb's law (magnetic)|Coulomb's law]], where '''H''' played a pivotal role and '''B''' was an auxiliary field, which explains its historic name "magnetic induction". At present the roles have swapped and some authors give '''B''' the name magnetic field (and do not give a name to '''H''' other than "auxiliary field"). | |||
In | In the general case, '''H''' is introduced in terms of '''B''' as: | ||
:<math> | |||
\begin{align} | |||
\mathbf{H} &= \frac{1}{\mu_0} \mathbf{B} - \mathbf{M}\qquad& \hbox{in SI units}\\ | |||
\mathbf{H} &= \mathbf{B} - 4\pi \mathbf{M}\qquad\;\; & \hbox{in Gaussian units},\\ | |||
\end{align} | |||
</math> | |||
with '''M'''('''r''', ''t'') the [[magnetization]] of the medium. | |||
For the most common case of linear materials, '''M''' is linear in '''H''',<ref> | |||
Some materials exhibit nonlinearity; that is, second and higher powers of '''H''' appear in the relation between '''M''' and '''H''', and hence, between '''B''' and '''H'''. At strong fields, such nonlinearity is found in most materials. | |||
</ref> and in [[SI|SI units]], | |||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
\mathbf{B} = \mu_0(\mathbf{1} + \boldsymbol{\chi}) \mathbf{H}, | \mathbf{B} = \mu_0(\mathbf{1} + \boldsymbol{\chi}) \mathbf{H}, | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
where '''1''' is the 3×3 unit matrix, '''χ''' the magnetic susceptibility tensor, and μ<sub>''0''</sub> the magnetic permeability of the vacuum ([[magnetic constant]]). | where '''1''' is the 3×3 [[unit matrix]], '''χ''' the magnetic susceptibility tensor of the magnetizable medium, and μ<sub>''0''</sub> the magnetic permeability of the vacuum (also known as [[magnetic constant]]). | ||
In [[Gaussian units]] the relation is | |||
:<math> | |||
\mathbf{B} = (\mathbf{1} + 4\pi \boldsymbol{\chi}) \mathbf{H}, | |||
</math> | |||
Many non-ferromagnetic materials are linear and isotropic; in the isotropic case the susceptibility tensor is equal to χ<sub>''m''</sub>'''1''', and '''H''' can easily be solved (in SI units) | |||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
\mathbf{H} = \frac{\mathbf{B}}{\mu_0 (1+\chi_m)} \equiv \frac{\mathbf{B}}{\mu_0 \mu_r}, | \mathbf{H} = \frac{\mathbf{B}}{\mu_0 (1+\chi_m)} \equiv \frac{\mathbf{B}}{\mu_0 \mu_r}, | ||
| Line 26: | Line 38: | ||
with the ''relative magnetic permeability'' μ<sub>''r''</sub> = 1 + χ<sub>''m''</sub>. | with the ''relative magnetic permeability'' μ<sub>''r''</sub> = 1 + χ<sub>''m''</sub>. | ||
For example, at standard temperature and pressure [[Reference conditions of gas temperature and pressure|(STP)]] [[air]], a mixture of [[paramagnetic]] [[oxygen]] and [[diamagnetic]] [[nitrogen]], is paramagnetic (i.e., has positive χ<sub>''m''</sub>), the χ<sub>''m''</sub> of air is 4⋅10<sup>−7</sup>. Argon at STP is diamagnetic with χ<sub>''m''</sub> = −1⋅10<sup>−8</sup>. For most [[ferromagnetic]] materials χ<sub>''m''</sub> depends on '''H''', with a non-linear relation between '''H''' and '''B''' and is large (depending on the material) from, say, 50 to 10000 and strongly varying as a function of '''H'''. | |||
The magnetic flux density '''B''' is a solenoidal (divergence-free, transverse) [[vector field]] because of one of [[Maxwell's equations]] | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{\nabla}\cdot\mathbf{B} = 0 \ , | |||
</math> | |||
This equation denies the existence of magnetic monopoles (magnetic charges) and hence also of magnetic currents. | |||
The magnetic field '''H''' is not necessarily solenoidal, however, because it satisfies: | |||
:<math>\boldsymbol{\nabla}\cdot\mathbf{H} = -\boldsymbol{\nabla}\cdot\mathbf{M} \ , | |||
</math> | |||
which need not be zero, although it will be zero in some common cases, for example, when '''B''' = μ'''H'''. The ''H''-field also exhibits discontinuity conditions at interfaces between media that may cause it to be non-solenoidal. | |||
===Example=== | |||
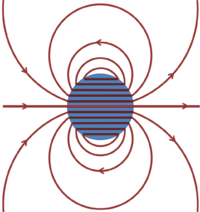
{{Image|Magnetized sphere.PNG|right|200px|'''B'''-field lines near a sphere uniformly magnetized in the horizontal direction}} | |||
To illustrate the roles of '''B''' and '''H''' a classic example is a sphere with uniform magnetization in an applied external uniform external magnetic flux density '''B'''.<ref name=Cloud> | |||
This derivation follows {{cite book |title=Electromagnetics |author=Edward J. Rothwell, Michael J. Cloud |url=http://books.google.com/books?id=jCqv1UygjA4C&pg=PA176 |pages=pp. 176 ''ff'' |chapter=§3.3.7 Magnetic field of a permanently magnetized body |isbn=084931397X |year=2001 |publisher=CRC Press}} This source provides two other methods for solving this problem. | |||
</ref> The figure shows the lines of the '''B'''-field when no external field is present; because '''B''' is solenoidal, field lines are closed. Outside the sphere, as shown below, the field is that of a magnetic dipole. To this dipole field, at the end of this example, a uniform external field is added oriented along the magnetization direction. | |||
To begin, the fields introduced by the magnetized sphere alone are found. Because no conduction or displacement currents are present, the magnetic field '''H''' satisfies: | |||
:<math>\mathrm{curl}\ \mathbf H = 0 \ , </math> | |||
which allows the introduction of a potential Φ:<ref name=Helmholtz> | |||
The representation of an irrotational (curl free) vector field by a scalar potential is a consequence of [[Helmholtz decomposition]]: see {{cite book |title=Engineering electromagnetics |author=Nathan Ida |year=2004|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=2CbvXE4o5swC&pg=PA698 |pages=p. 698 |isbn=0387201564 |edition=2nd ed |publisher=Springer}} | |||
</ref> | |||
:<math>\mathbf H = -\ \mathrm{grad}\ \Phi \ .</math> | |||
Taking the divergence, and using the zero divergence of '''B''': | |||
:<math>\nabla ^2 \Phi =\mathrm{div} \mathbf M \ , </math> | |||
which is [[Coulomb%27s_law#Poisson_equation|Poisson's equation]]. For constant '''M''', div '''M''' = 0. However, the solutions inside and outside the sphere must satisfy the boundary conditions on the sphere's surface that the normal component of '''B''' is continuous: | |||
:<math>\mathbf{ \hat{u} _{12} \cdot}\left(\mathbf{B_1-B_2}\right) =\mathbf{ \hat{u} _{12} \cdot} \mu_0\left(\mathbf{H_1+M_1 -H_2-M_2}\right) =0 \ , </math> | |||
while the normal component of '''H''' may be discontinuous if there exist surface "magnetic" charges, σ<sub>1</sub> and σ<sub>2</sub>, that is: | |||
:<math>\mathbf{ \hat{u} _{12} \cdot}\left(\mathbf{H_1-H_2}\right) =\sigma_1+\sigma_2 \ , </math> | |||
where unit vector '''û<sub>12</sub>''' points into region 2 from region 1. Taking region 1 inside the sphere where '''M<sub>1</sub>''' = '''M''' and region 2 outside where '''M<sub>2</sub>'''=0 and σ<sub>2</sub> = 0, | |||
:<math>\mathbf{ \hat{u} _{12} \cdot} \mu_0\left(\mathbf{H_1+M -H_2 }\right) =0 \ , </math> | |||
or: | |||
:<math>\mathbf{ \hat{u} _{12} \cdot} \left(\mathbf{H_1 -H_2 }\right) = -\mathbf{ \hat{u} _{12} \cdot M} \ =\sigma_1 . </math> | |||
The solution to Poisson's equation with this surface charge is (see [[Coulomb%27s_law#Poisson_equation|Poisson's equation]]): | |||
:<math> | |||
\begin{align} | |||
\Phi(\mathbf{r}) &= \iint _{S} \frac{\sigma_1(\mathbf{r'})}{4\pi|\mathbf{r} - \mathbf{r'}|} d{S'}\\ | |||
&=\int _{-\pi}^{\pi}\sin \theta ' d \theta ' \int_0^\pi d\phi ' \frac{M \cos \theta '}{4\pi |\mathbf{r} - \mathbf{r'}|}\\ | |||
&= \frac{M}{3} R^2 \cos \theta \frac {r_<} {r_>^2} \ , | |||
\end{align} | |||
</math> | |||
with ''R'' the radius of the sphere and ''r<sub><</sub>'' referring to the minimum of ''r'' and ''R'', ''r<sub>></sub> '' to the maximum of ''r'' and ''R''. The magnetic field is given inside the sphere by the gradient as: | |||
:<math>\mathbf{H} = -\frac{M}{3}\mathbf{ \hat{u}_z}\ ,\ \mathbf B =\mu_0 \frac{2M}{3} \mathbf{ \hat{u}_z} </math> | |||
with '''û<sub>z</sub>''' a unit vector in the horizontal direction of magnetization. Evidently, the magnetic field '''H''' points oppositely to the magnetic flux '''B''' inside the sphere. Outside the sphere the field is that of a magnetic dipole: | |||
:<math>\mathbf H = \frac{M R^3}{3r^3}\left(\hat{\mathbf{ r}}\ 2 \cos \theta + \hat{\boldsymbol{ \theta}} \sin \theta \right) \ , \ \mathbf B = \mu_0 \mathbf H \ . </math> | |||
In particular, along the horizontal ''z''-axis, θ = 0, and the magnetic field outside the sphere along its axis is: | |||
:<math>\mathbf{H} = \frac{2M}{3}\mathbf{ \hat{u}_z}\ ,\ \mathbf{B} = \mu_0\frac{2M}{3}\mathbf{ \hat{u}_z}\ ,</math> | |||
showing the continuity of the normal component of '''B'''. | |||
If an external magnetic field is imposed, '''H<sub>a</sub>''' = H<sub>a</sub>'''û<sub>z</sub>''' it can be added to the zero field solution above. Then, inside the sphere the magnetic field '''H''' is '''H<sub>a</sub> − M'''/3. The geometric factor 1/3, which depends upon the shape of the object being a sphere, is called the "demagnetizing factor". | |||
==Notes== | |||
<references />[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:01, 14 September 2024
In physics, a magnetic field (commonly denoted by H) describes a magnetic field (a vector) at every point in space; it is a vector field. In non-relativistic physics, the space in question is the three-dimensional Euclidean space —the infinite world that we live in.
In general H is seen as an auxiliary field useful when a magnetizable medium is present. The magnetic flux density B is usually seen as the fundamental magnetic field, see the article about B for more details about magnetism.
The SI unit of magnetic field strength is ampere⋅turn/meter; a unit that is based on the magnetic field of a solenoid. In the Gaussian system of units |H| has the unit oersted, with one oersted being equivalent to (1000/4π)⋅A⋅turn/m.
Relation between H and B
The magnetic field H is closely related to the magnetic induction B (also a vector field). It is the vector B that enters the expression for magnetic force on moving charges (Lorentz force). Historically, the theory of magnetism developed from Coulomb's law, where H played a pivotal role and B was an auxiliary field, which explains its historic name "magnetic induction". At present the roles have swapped and some authors give B the name magnetic field (and do not give a name to H other than "auxiliary field").
In the general case, H is introduced in terms of B as:
with M(r, t) the magnetization of the medium.
For the most common case of linear materials, M is linear in H,[1] and in SI units,
where 1 is the 3×3 unit matrix, χ the magnetic susceptibility tensor of the magnetizable medium, and μ0 the magnetic permeability of the vacuum (also known as magnetic constant). In Gaussian units the relation is
Many non-ferromagnetic materials are linear and isotropic; in the isotropic case the susceptibility tensor is equal to χm1, and H can easily be solved (in SI units)
with the relative magnetic permeability μr = 1 + χm.
For example, at standard temperature and pressure (STP) air, a mixture of paramagnetic oxygen and diamagnetic nitrogen, is paramagnetic (i.e., has positive χm), the χm of air is 4⋅10−7. Argon at STP is diamagnetic with χm = −1⋅10−8. For most ferromagnetic materials χm depends on H, with a non-linear relation between H and B and is large (depending on the material) from, say, 50 to 10000 and strongly varying as a function of H.
The magnetic flux density B is a solenoidal (divergence-free, transverse) vector field because of one of Maxwell's equations
This equation denies the existence of magnetic monopoles (magnetic charges) and hence also of magnetic currents.
The magnetic field H is not necessarily solenoidal, however, because it satisfies:
which need not be zero, although it will be zero in some common cases, for example, when B = μH. The H-field also exhibits discontinuity conditions at interfaces between media that may cause it to be non-solenoidal.
Example
To illustrate the roles of B and H a classic example is a sphere with uniform magnetization in an applied external uniform external magnetic flux density B.[2] The figure shows the lines of the B-field when no external field is present; because B is solenoidal, field lines are closed. Outside the sphere, as shown below, the field is that of a magnetic dipole. To this dipole field, at the end of this example, a uniform external field is added oriented along the magnetization direction.
To begin, the fields introduced by the magnetized sphere alone are found. Because no conduction or displacement currents are present, the magnetic field H satisfies:
which allows the introduction of a potential Φ:[3]
Taking the divergence, and using the zero divergence of B:
which is Poisson's equation. For constant M, div M = 0. However, the solutions inside and outside the sphere must satisfy the boundary conditions on the sphere's surface that the normal component of B is continuous:
while the normal component of H may be discontinuous if there exist surface "magnetic" charges, σ1 and σ2, that is:
where unit vector û12 points into region 2 from region 1. Taking region 1 inside the sphere where M1 = M and region 2 outside where M2=0 and σ2 = 0,
or:
The solution to Poisson's equation with this surface charge is (see Poisson's equation):
with R the radius of the sphere and r< referring to the minimum of r and R, r> to the maximum of r and R. The magnetic field is given inside the sphere by the gradient as:
with ûz a unit vector in the horizontal direction of magnetization. Evidently, the magnetic field H points oppositely to the magnetic flux B inside the sphere. Outside the sphere the field is that of a magnetic dipole:
In particular, along the horizontal z-axis, θ = 0, and the magnetic field outside the sphere along its axis is:
showing the continuity of the normal component of B.
If an external magnetic field is imposed, Ha = Haûz it can be added to the zero field solution above. Then, inside the sphere the magnetic field H is Ha − M/3. The geometric factor 1/3, which depends upon the shape of the object being a sphere, is called the "demagnetizing factor".
Notes
- ↑ Some materials exhibit nonlinearity; that is, second and higher powers of H appear in the relation between M and H, and hence, between B and H. At strong fields, such nonlinearity is found in most materials.
- ↑ This derivation follows Edward J. Rothwell, Michael J. Cloud (2001). “§3.3.7 Magnetic field of a permanently magnetized body”, Electromagnetics. CRC Press, pp. 176 ff. ISBN 084931397X. This source provides two other methods for solving this problem.
- ↑ The representation of an irrotational (curl free) vector field by a scalar potential is a consequence of Helmholtz decomposition: see Nathan Ida (2004). Engineering electromagnetics, 2nd ed. Springer, p. 698. ISBN 0387201564.