Blast (explosives): Difference between revisions
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz No edit summary |
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
| id = TM 9-1300-214 | | id = TM 9-1300-214 | ||
| publisher = [[U.S. Department of the Army]] | | publisher = [[U.S. Department of the Army]] | ||
| date = September 1984 | title = Military Explosives}}, p. 4-11 to 4-13</ref> | | date = September 1984 | title = Military Explosives}}, p. 4-11 to 4-13</ref> While the emphasis here is on the gases and the shock wave, explosive blast also produces thermal effects, light and sound, with additional and stronger effects from nuclear weapons.<ref name=FEMA>{{citation | ||
| url = http://www.fema.gov/pdf/plan/prevent/rms/428/fema428_ch4.pdf | |||
| chapter = Chapter 4, Explosive Blast | |||
| id = FEMA 428 | |||
| title = Primer to Design Safe School Projects in Case of Terrorist Attacks | |||
| journal = [[Federal Emergency Management Agency]]}}</ref> The preliminary discussion also assumes the blast takes place near the ground, since, even with high explosives, the [[Mach effect]] can cause complex interactions of reinforcement of transmitted and reflected shock waves from bursts above the ground. | |||
[[Image:Pressure-vs-time in blast.png|left|450px|thumb|Pressure vs. time in air explosion]] | [[Image:Pressure-vs-time in blast.png|left|450px|thumb|Pressure vs. time in air explosion]] | ||
The inertia of these gases are prevented, by their inertia, from slowing abruptly at the shock front, but rarefaction still take place, and a low-pressure region may follow behind the leading edge of the gases. Indeed, there may even be a lower-than-atmospheric area further behind, and a vacuum area produces. "When the pressure becomes less than atmospheric, the wind reverses in direction and blows backward toward the point of detonation. Any light object, such as a leaf, when struck by the shock front, is rapidly carried away from the point of detonation and then is blown back almost to the original position when the wind reverses." In especially hot explosions, the heating of the air and its consequence reduction and density becomes important, especially in [[nuclear weapons|nuclear explosions]]. | The inertia of these gases are prevented, by their inertia, from slowing abruptly at the shock front, but rarefaction still take place, and a low-pressure region may follow behind the leading edge of the gases. Indeed, there may even be a lower-than-atmospheric area further behind, and a vacuum area produces. "When the pressure becomes less than atmospheric, the wind reverses in direction and blows backward toward the point of detonation. Any light object, such as a leaf, when struck by the shock front, is rapidly carried away from the point of detonation and then is blown back almost to the original position when the wind reverses." In especially hot explosions, the heating of the air and its consequence reduction and density becomes important, especially in [[nuclear weapons|nuclear explosions]]. There may even be circumstances, however, where strong structures such as walls are pulled backward by a negative force. | ||
==Effects== | ==Effects== | ||
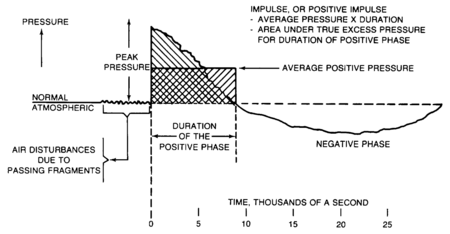
Blast effect is measured by two criteria, | Blast effect is measured by two criteria, peak pressure and impulse. | ||
peak pressure and impulse. Peak pressure is the | *Peak pressure is the pressure increase at the shock front or the highest pressure in the shock wave minus atmospheric pressure. Peak pressure represents a measure of | ||
pressure increase at the shock front or the highest | |||
pressure in the shock wave minus atmospheric | |||
the maximum force exerted against a surface by a blast | the maximum force exerted against a surface by a blast | ||
wave, since force is equal to the product of pressure and | wave, since force is equal to the product of pressure and | ||
area. Impulse represents a measure of the force | area. | ||
*Impulse is mathematically equal to the area under the time pressure curve for the duration of the positive phase. This is approximately half the peak pressure multiplied by the duration of the positive phase. Impulse represents a measure of the force | |||
multiplied by the duration." | multiplied by the duration." | ||
| Line 46: | Line 30: | ||
==Solid== | ==Solid== | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
Revision as of 16:51, 26 April 2010
Blast is the process by which explosives, in a millisecond or less, are converted to hot explosive gases. Depending on the construction of the container holding the explosive, as much as half the force may go into disrupting it rather than producing effects; the strongest cases are military warheads and gravity bombs.
Blast effects are most complex in air, although they are not trivial in air or in solids. Indeed, there is a complex discipline of forming solid structures with explosive waves, perhaps most complex in the compression systems of nuclear weapons.
Air
- See also: Mach effect
At the leading edge of the detonation is a sharply delineated reagion called the shock front, in which the pressure rises dramatically. Its initial velocity is much greater than sound but drops dramatically. The gases of detonation follow it.[1] While the emphasis here is on the gases and the shock wave, explosive blast also produces thermal effects, light and sound, with additional and stronger effects from nuclear weapons.[2] The preliminary discussion also assumes the blast takes place near the ground, since, even with high explosives, the Mach effect can cause complex interactions of reinforcement of transmitted and reflected shock waves from bursts above the ground.
The inertia of these gases are prevented, by their inertia, from slowing abruptly at the shock front, but rarefaction still take place, and a low-pressure region may follow behind the leading edge of the gases. Indeed, there may even be a lower-than-atmospheric area further behind, and a vacuum area produces. "When the pressure becomes less than atmospheric, the wind reverses in direction and blows backward toward the point of detonation. Any light object, such as a leaf, when struck by the shock front, is rapidly carried away from the point of detonation and then is blown back almost to the original position when the wind reverses." In especially hot explosions, the heating of the air and its consequence reduction and density becomes important, especially in nuclear explosions. There may even be circumstances, however, where strong structures such as walls are pulled backward by a negative force.
Effects
Blast effect is measured by two criteria, peak pressure and impulse.
- Peak pressure is the pressure increase at the shock front or the highest pressure in the shock wave minus atmospheric pressure. Peak pressure represents a measure of
the maximum force exerted against a surface by a blast wave, since force is equal to the product of pressure and area.
- Impulse is mathematically equal to the area under the time pressure curve for the duration of the positive phase. This is approximately half the peak pressure multiplied by the duration of the positive phase. Impulse represents a measure of the force
multiplied by the duration."
Water
Solid
References
- ↑ Military Explosives, U.S. Department of the Army, September 1984, TM 9-1300-214, p. 4-11 to 4-13
- ↑ , Chapter 4, Explosive Blast"Primer to Design Safe School Projects in Case of Terrorist Attacks", Federal Emergency Management Agency, FEMA 428