Thylakoid: Difference between revisions
imported>Anthony.Sebastian (add ref) |
imported>Anthony.Sebastian (format edit; content addition.) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
The molecular clusters in the grana and stromal thylakoid membranes transfer the energy of the energized electrons to energy-carrier molecules—[[Adenosine triphosphate|ATP]] and [[NADPH]]—the energy therein used in metabolic reactions in the stroma to synthesize organic compounds using the inorganic carbon compound, carbon dioxide, as the carbon source starting material.<ref name=ftexplorethylakoid> [http://www.ftexploring.com/photosyn/chloroplast.html#THYLAKOID Thylakoid]. FT Exploring. Where and how photosynthesis occurs in a typical leaf. | The molecular clusters in the grana and stromal thylakoid membranes transfer the energy of the energized electrons to energy-carrier molecules—[[Adenosine triphosphate|ATP]] and [[NADPH]]—the energy therein used in metabolic reactions in the stroma to synthesize organic compounds using the inorganic carbon compound, carbon dioxide, as the carbon source starting material.<ref name=ftexplorethylakoid> [http://www.ftexploring.com/photosyn/chloroplast.html#THYLAKOID Thylakoid]. FT Exploring. Where and how photosynthesis occurs in a typical leaf. | ||
*<font face="Gill Sans MT">Scroll to section, 'THYLAKOIDS'</font></ref> In generating ATP, | *<font face="Gill Sans MT">Scroll to section, 'THYLAKOIDS'</font></ref> | ||
In generating ATP, molecules in the thylakoids' electron transfer chains pump protons from the stroma to the thylakoid lumen, making the lumen more acidic. The higher lumen concentration of protons compared to that in the stroma leads to protons passing back into the stroma through a pathway in the enzyme, ATP synthase, a complex molecule in the thylakaloid membrane that utilizes the energy inherent in the proton concentration gradient to synthesize ATP, converting ADP to ATP. ATP is a key energy source for synthesizing organic compounds from carbon dioxide in the stroma, a phase of the photosynthetic process called the [[Calvin cycle]].<ref name=ftexplorethylakoid/> | |||
In generating NADPH from NADP, a [[Redox|redox]] reaction, NADPH becomes an energy-rich electron-carrier that supplies electrons for [[Redox|reducing]] carbon dioxide to carbohydrates as part of the Calvin cycle in the stroma. Thus the light-dependent photosynthetic reactions in the thylakoid membranes supply both the ATP and NADPH, energy and electrons for stromal light-independent synthesis of carbohydrate. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 16:27, 6 December 2010
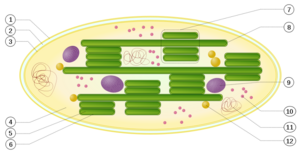
Schematic of a chloroplast: 1. outer membrane; 2. intermembrane space; 3. inner membrane (1+2+3: envelope); 4. [stroma (aqueous fluid); 5. thylakoid lumen (inside of thylakoid); 6. thylakoid membrane; 7. granum (stack of thylakoids); 8. thylakoid (lamella); 9. Starch; 10. Ribosome; 11. plastidial DNA; 12. plastoglobule (drop of lipids).
Inside plant cells and other eukaryotic cells that perform photosynthesis, tiny, bacteria-sized organelles, called chloroplasts, contain, within the inner membrane of their dual membrane structure, an extensive system of single-membrane-bound flattened sacs called thylakoids, their interior spaces (lumens) interconnected, their membranes housing the pigment molecules that absorb the energy of photons of particular frequencies emitted by the sun, an event that initiates the physico-chemical sequence of steps culminating in the products of photosynthesis.[2] A semifluid matrix within the chloroplasts, called the stroma, bathes the thylakoids. The flattened thylakoid sacs consist of clustered stacks, called grana, their lumens interconnected by extensions, called 'stromal thylakoids', or lamellae.[3] [See accompanying illustration at right.]
The illustration does not due justice to the complexity of the thylakoid structure:Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; invalid names, e.g. too many [3]
Grana consist of cylindrical stacks of ~10 to 20 tightly appressed thylakoids of 300 to 600 nm in diameter that are interconnected by single, unstacked, stroma thylakoids….the stroma [thylakoid] membranes are wound around the granum in the form of multiple right-handed helices, in which each granum thylakoid is connected to an average of eight stroma thylakoids…The cylindrical granum pillar of stacked membranes is surrounded by multiple helices of stroma thylakoids that are interconnected via slits or junctions at the margins of the grana, which ensures the contiguity of the thylakoid membranes and their lumenal aqueous phases across the entire granum-stroma network. [3]
The grana thylakoid membranes possess the molecular structures for one segment of the photosystem (photosystem II), the stromal thylakoid mmbranes, the molecular structures for another segment (photosystem I), with the lumens one continuous space.[3]
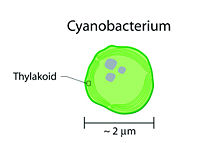
Prokaryotic cells that carry out photosynthesis (e.g., cyanobacteria) do not contain chloroplasts; their thylakoid membranes reside within the cytoplasm of the cells, as shown in the accompanying figure at left.[4] [5]
In general terms, the photosynthetic process enables the energy of photons radiated from the sun to energize electrons in special photon-absorbing pigment molecules embedded in the thylakoid membranes, electrons ultimately supplied by the splitting of water molecules in a reaction that also converts water's oxygen atoms to molecular oxygen for release into the atmosphere and for use by the plant.
The molecular clusters in the grana and stromal thylakoid membranes transfer the energy of the energized electrons to energy-carrier molecules—ATP and NADPH—the energy therein used in metabolic reactions in the stroma to synthesize organic compounds using the inorganic carbon compound, carbon dioxide, as the carbon source starting material.[6]
In generating ATP, molecules in the thylakoids' electron transfer chains pump protons from the stroma to the thylakoid lumen, making the lumen more acidic. The higher lumen concentration of protons compared to that in the stroma leads to protons passing back into the stroma through a pathway in the enzyme, ATP synthase, a complex molecule in the thylakaloid membrane that utilizes the energy inherent in the proton concentration gradient to synthesize ATP, converting ADP to ATP. ATP is a key energy source for synthesizing organic compounds from carbon dioxide in the stroma, a phase of the photosynthetic process called the Calvin cycle.[6]
In generating NADPH from NADP, a redox reaction, NADPH becomes an energy-rich electron-carrier that supplies electrons for reducing carbon dioxide to carbohydrates as part of the Calvin cycle in the stroma. Thus the light-dependent photosynthetic reactions in the thylakoid membranes supply both the ATP and NADPH, energy and electrons for stromal light-independent synthesis of carbohydrate.
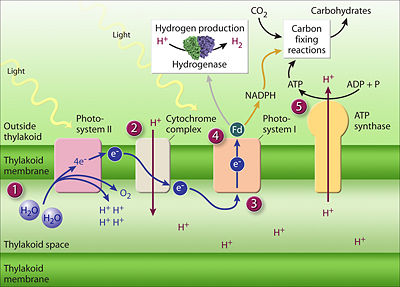 (PD) Drawing: http://genomics.energy.gov/. Genome Management Information System, Oak Ridge National Laboratory. http://genomicscience.energy.gov/roadmap/ Genomics:GTL Roadmap, U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science, August 2005. See text in preceding paragraph and legend-box at right. |
|
References
- ↑ Morton O. (2008) Eating the Sun: How Plants Power the Planet. HarperColins. ISBN 0007163649 , ISBN 978-0007163649.
- ↑ Chloroplasts. | Additional information about chloroplasts and thylakoids.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Mustardy L, Buttle K, Steinbach G, Garab G. (2008) The three-dimensional network of the thylakoid membranes in plants: quasihelical model of the granum-stroma assembly. Plant Cell 20:2552-7.
- View also the supplementary figures and video linked in this paper.
- ↑ Typical cell of a cyanobacterium, a photosynthesis-capable prokaryote.
- Scroll down to Figure 4, showing the thylakoids, labelled 'photosynthetic membranes', as extensions of the cell membrane. Although cyanobacteria contain no chloroplasts, the cells themselves resemble eukaryotic chloroplasts.
- ↑ Barton L. (2005) Structural and functional relationships in prokaryotes. New York: Springer, ISBN 9780387271255. | Discusses thylakoids in cyanobacteria
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Thylakoid. FT Exploring. Where and how photosynthesis occurs in a typical leaf.
- Scroll to section, 'THYLAKOIDS'