Acceleration due to gravity: Difference between revisions
imported>'Dragon' Dave McKee mNo edit summary |
imported>'Dragon' Dave McKee mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Considering a body with the mass ''M'' as a source of a gravitational field, the strength of that field, or the | Considering a body with the mass ''M'' as a source of a gravitational field, the strength of that field, or the | ||
gravitational acceleration, is given by <math>\vec g = -G \frac{M}{r^2} \frac{\ | gravitational acceleration, is given by <math>\vec g = -G \frac{M}{r^2} \frac{\vec{r}}{r}</math>. | ||
The modulus of ''g'' is <math>g = G \frac{M}{r^2}</math>. | The modulus of ''g'' is <math>g = G \frac{M}{r^2}</math>. | ||
Revision as of 20:16, 23 February 2008
Considering a body with the mass M as a source of a gravitational field, the strength of that field, or the gravitational acceleration, is given by . The modulus of g is .
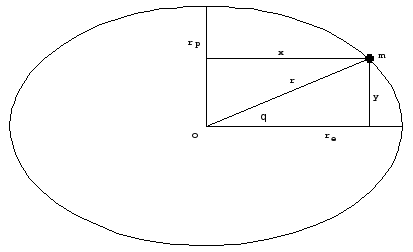
Here G is the gravitational constant, G = 6.67428×10-11 Nm2/kg2, r is the distance between a body of mass m and the center of the gravitational field, is the vector radius of that body having the mass m. If the source of the gravitational field has a spherical shape, then r is the sphere’s radius. Taking into account that the Earth is an oblate spheroid, the distance r is not that of a sphere and varies from the equator to the poles.
A normal section (on the equatorial plane) is almost an ellipse, so, r can be done by:
where re and rp are the equatorial radius and polar radius, respectively and θ is the latitude, or
the angle made by r with the equatorial plane.
References
1. V.Dorobantu and Simona Pretorian, Physics between fear and respect, Vol. 3, Edited by Politehnica
Timisoara, 2007, ISBN 978-973-625-493-2