File:NMDA receptor.jpg: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
imported>Caesar Schinas m (Robot: Changing template: PD-USgov) |
imported>Caesar Schinas m (Bot: Replace Template:Image_notes_* with Template:Image_Details) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Summary == | == Summary == | ||
{{ | {{Image_Details | ||
| | |description = Activation (i.e., excitation) occurs when either glutamate (Glu) or N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) and glycine (Gly) bind to the receptor molecule. A channel within the receptor complex enables molecules to cross the cell membrane. Magnesium (Mg) blocks this channel. When Mg is removed from the channel and the receptor is activated, calcium (Ca++) and sodium (Na+) ions enter the cell and potassium ions (K+) leave. MK-801 prevents the flow of ions across the membrane by binding to a site within the ion channel, thereby blocking NMDA receptor function and protecting the cell against excess activation (i.e., excitotoxicity). | ||
| | |author = J.D. Thomas and E.P. Riley | ||
| | |copyright = National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism | ||
| | |source = http://www.niaaa.nih.gov/Resources/GraphicsGallery/Neuroscience/221p51.htm | ||
| | |date-created = 1998 | ||
| | |pub-country = United States | ||
| | |notes = | ||
| | |versions = | ||
}} | |||
== Licensing/Copyright status == | == Licensing/Copyright status == | ||
{{PD|usgov}} | {{PD|usgov}} | ||
Revision as of 03:18, 22 June 2009
Summary
| Title / Description
|
Activation (i.e., excitation) occurs when either glutamate (Glu) or N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) and glycine (Gly) bind to the receptor molecule. A channel within the receptor complex enables molecules to cross the cell membrane. Magnesium (Mg) blocks this channel. When Mg is removed from the channel and the receptor is activated, calcium (Ca++) and sodium (Na+) ions enter the cell and potassium ions (K+) leave. MK-801 prevents the flow of ions across the membrane by binding to a site within the ion channel, thereby blocking NMDA receptor function and protecting the cell against excess activation (i.e., excitotoxicity). |
|---|---|
| Author(s)
|
J.D. Thomas and E.P. Riley |
| Copyright holder
|
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism See below for license/re-use information. |
| Source
|
http://www.niaaa.nih.gov/Resources/GraphicsGallery/Neuroscience/221p51.htm |
| Date created
|
1998 |
| Country of first publication
|
United States |
| Notes
|
You can edit this page and add notes here which may be useful to people who wish to re-use this media. |
| Other versions
|
If there are other versions of this media on CZ, please list them here. |
| Using this image on CZ
|
Copy the code below to add this image to a Citizendium article, changing the size, alignment, and caption as necessary.
|
Image issue? Contact us via the email below.
Please send email to manager A T citizendium.org .
Licensing/Copyright status
This media, NMDA receptor.jpg, is in the public domain
This is a work of the United States Government, and as such is not afforded copyright protection under US law.
For further information see Title 17, Chapter 1, Section 105 of the US Code.
You may freely copy, distribute, display and perform this work, as well as make derivative and commercial works.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 18:56, 11 March 2022 | 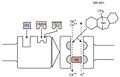 | 788 × 508 (67 KB) | Maintenance script (talk | contribs) | == Summary == Importing file |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: