Tioconazole: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk (New page: {{subpages}} {{Chem infobox |align=right |image=center|thumb|200px |width=350px |molname=tioconazole |synonyms= Tioconazol, Tioconazolum |molformula= C<sub>16</...) |
imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|align=right | |align=right | ||
|image=[[Image:Tioconazole.jpg|center|thumb|200px]] | |image=[[Image:Tioconazole.jpg|center|thumb|200px]] | ||
|width= | |width=200px | ||
|molname=tioconazole | |molname=tioconazole | ||
|synonyms= Tioconazol, Tioconazolum | |synonyms= Tioconazol, Tioconazolum | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|casnumber=65899-73-2 | |casnumber=65899-73-2 | ||
}} | }} | ||
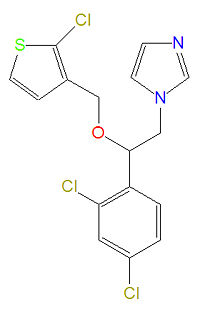
'''Tioconazole''' is broad-spectrum [[imidazole]]-based [[antifungal drug]] used to treat fungus and yeast infections that is used topically to treate [[althlete's foot]], [[jock itch]], [[ringworm]] and [[tinea versicolor]]. Like other [[azole]]-based antifungal agents, it inhibits 14-alpha-methylase, a cytochrome P-450 enzyme that converts [[lanosterol]] to [[ergosterol]], an essential component of the cell membrane. | '''Tioconazole''' is broad-spectrum [[imidazole]]-based [[antifungal drug]] used to treat fungus and yeast infections that is used topically to treate [[althlete's foot]], [[jock itch]], [[ringworm]] and [[tinea versicolor]]. Like other [[azole]]-based antifungal agents, it inhibits 14-alpha-methylase, a cytochrome P-450 enzyme that converts [[lanosterol]] to [[ergosterol]], an essential component of the cell membrane. | ||
== Mechanism of action == | == Mechanism of action == | ||
Tioconazole increases cell membrane permeability by inhibiting 14-alpha-methylase and thus nterefering with the conversion of laosterol to ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell wall membranes. Tioconazole may also inhibit endogenous respiration, interact with membrane phospholipids, inhibit the transformation of yeasts to mycelial forms and the uptake of purine, impair triglyceride and/or phospholipid biosynthesis, and inhibit the movement of calcium and potassium ions across the cell membrane by blocking the ion transport pathway known as the Gardos channel. | Tioconazole increases cell membrane permeability by inhibiting 14-alpha-methylase and thus nterefering with the conversion of laosterol to ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell wall membranes. Tioconazole may also inhibit endogenous respiration, interact with membrane phospholipids, inhibit the transformation of yeasts to mycelial forms and the uptake of purine, impair triglyceride and/or phospholipid biosynthesis, and inhibit the movement of calcium and potassium ions across the cell membrane by blocking the ion transport pathway known as the Gardos channel. | ||
Revision as of 11:15, 10 May 2008
|
| |||||||
| tioconazole | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antifungal drug | ||||||
| Properties: | azole compound | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Tioconazole is broad-spectrum imidazole-based antifungal drug used to treat fungus and yeast infections that is used topically to treate althlete's foot, jock itch, ringworm and tinea versicolor. Like other azole-based antifungal agents, it inhibits 14-alpha-methylase, a cytochrome P-450 enzyme that converts lanosterol to ergosterol, an essential component of the cell membrane.
Mechanism of action
Tioconazole increases cell membrane permeability by inhibiting 14-alpha-methylase and thus nterefering with the conversion of laosterol to ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell wall membranes. Tioconazole may also inhibit endogenous respiration, interact with membrane phospholipids, inhibit the transformation of yeasts to mycelial forms and the uptake of purine, impair triglyceride and/or phospholipid biosynthesis, and inhibit the movement of calcium and potassium ions across the cell membrane by blocking the ion transport pathway known as the Gardos channel.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include erythema, stinging, blistering, peeling, edema, pruritus, urticaria, burning, and general irritation of the skin, and cramps.
Brand names
Fungibacid® GyneCure® Gyno-trosyd® Monistat 1® Trosyd® Trosyd AF® Trosyd J® Trosyl® Tz-3® Vagistat® Vagistat-1® Zoniden®